Pathogens, Free Full-Text
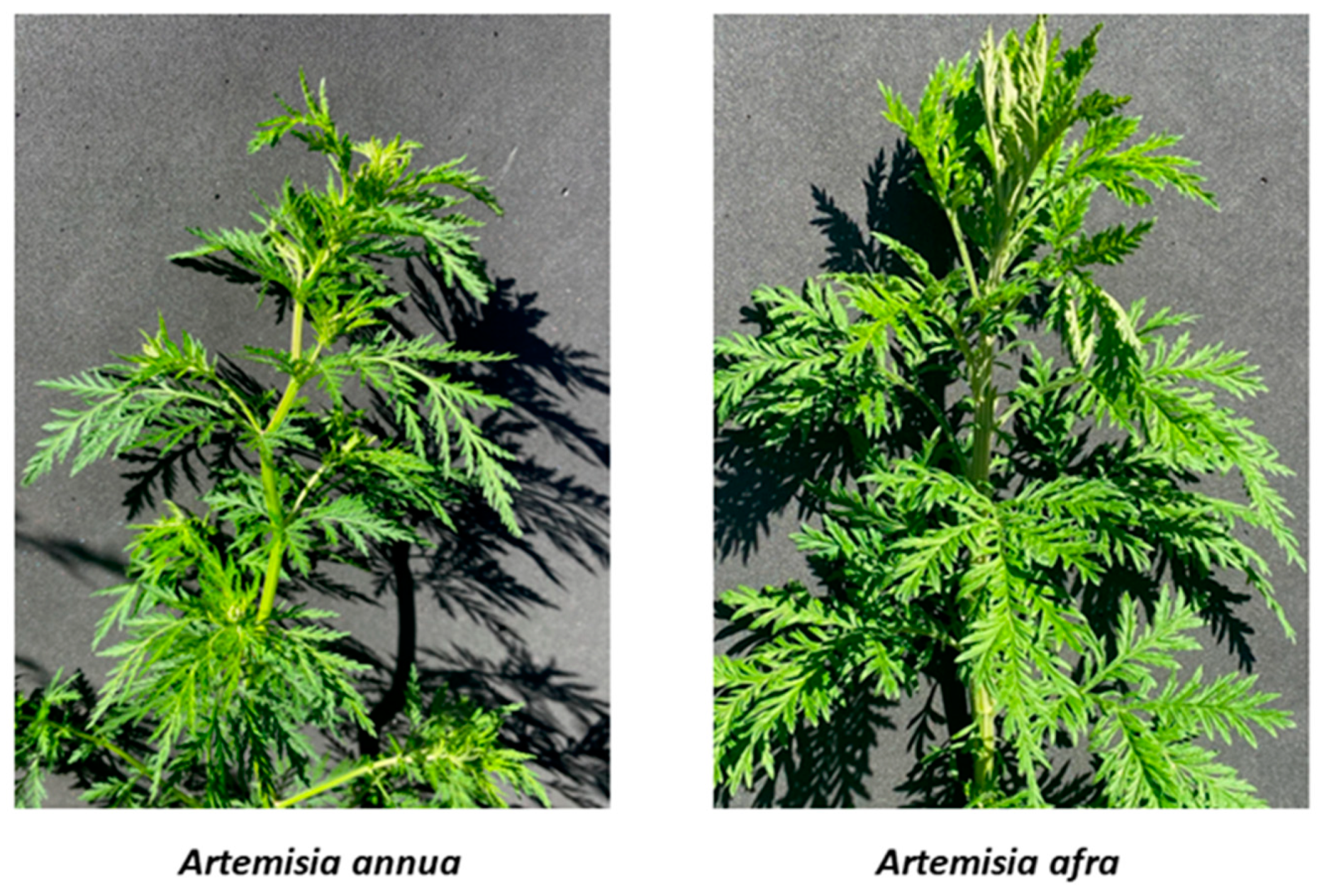

Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) is a deadly pathogen and causative agent of human tuberculosis, causing ~1.5 million deaths every year. The increasing drug resistance of this pathogen necessitates novel and improved treatment strategies. A crucial aspect of the host–pathogen interaction is bacterial nutrition. In this study, Artemisia annua and Artemisia afra dichloromethane extracts were tested for bactericidal activity against Mtb strain mc26230 under hypoxia and various infection-associated carbon sources (glycerol, glucose, and cholesterol). Both extracts showed significant bactericidal activity against Mtb, regardless of carbon source. Based on killing curves, A. afra showed the most consistent bactericidal activity against Mtb for all tested carbon sources, whereas A. annua showed the highest bactericidal activity in 7H9 minimal media with glycerol. Both extracts retained their bactericidal activity against Mtb under hypoxic conditions. Further investigations are required to determine the mechanism of action of these extracts and identify their active constituent compounds.
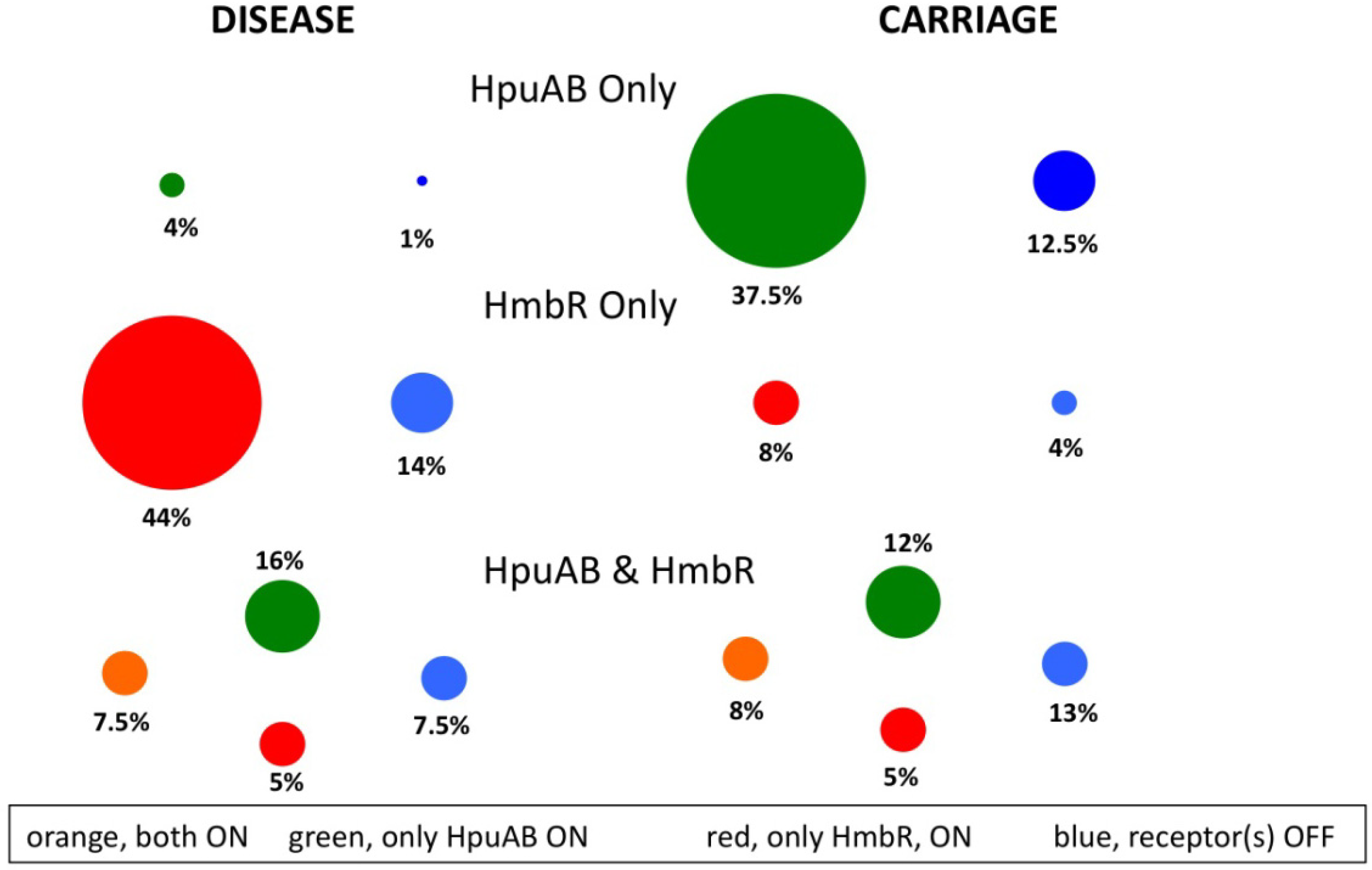
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Pathogens, Free Full-Text
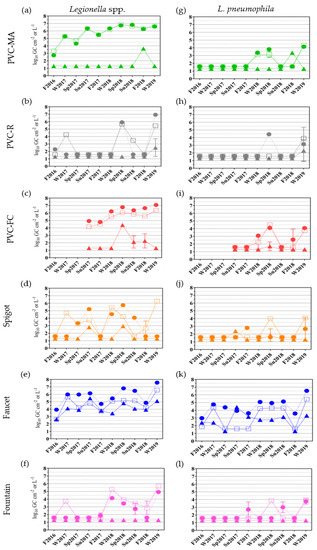
Pathogens, Free Full-Text, duda games gta rp

Pathogens Lesson - Bright in the Middle

Commensal bacteria in the upper respiratory tract regulate susceptibility to infection - ScienceDirect

Microorganisms, Free Full-Text, viana costa aguas claras

Bloodborne Pathogens Poster OSHA Safety Workplace Posters

What is a pathogen? - 4-H Animal Science

Pathogens, Free Full-Text, duda games gta rp

Mouse hygiene status–A tale of two environments for mast cells and allergy - ScienceDirect

Pathogens Packet - Bacteria Viruses Protozoa Fungi Parasites and Prions - Homeschool Den
Pathogens and Disease - Wiley Online Library

Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Pathogens and Disease